198 words
1 minutes
Getting Started with Postman
Postman is a tool for testing web APIs, allowing you to easily send requests such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. You can find and install it by searching the Chrome Web Store.
To demonstrate its features, let’s first start a local server:
var http = require("http");
var url = require("url");
var querystring = require("querystring");
http
.createServer(function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, { "content-type": "text/json" });
if (req.method === "GET") {
var params = url.parse(req.url, true).query;
res.write(params.name + " is " + params.age + " years old");
res.on("error", function (err) {
throw new Error(err);
});
res.end();
} else {
var resDate = [];
req
.on("data", function (chunk) {
resDate.push(chunk);
})
.on("end", function () {
var params = querystring.parse(resDate.join(""));
res.write(JSON.stringify(params));
res.end();
})
.on("error", function (e) {
throw new Error(e);
});
}
})
.listen(8088);
console.log("Server listen at localhost:8088");This server will listen for POST and GET requests and return the corresponding data. Next, open Postman. The interface is very clean, and all features are labeled in the image below. 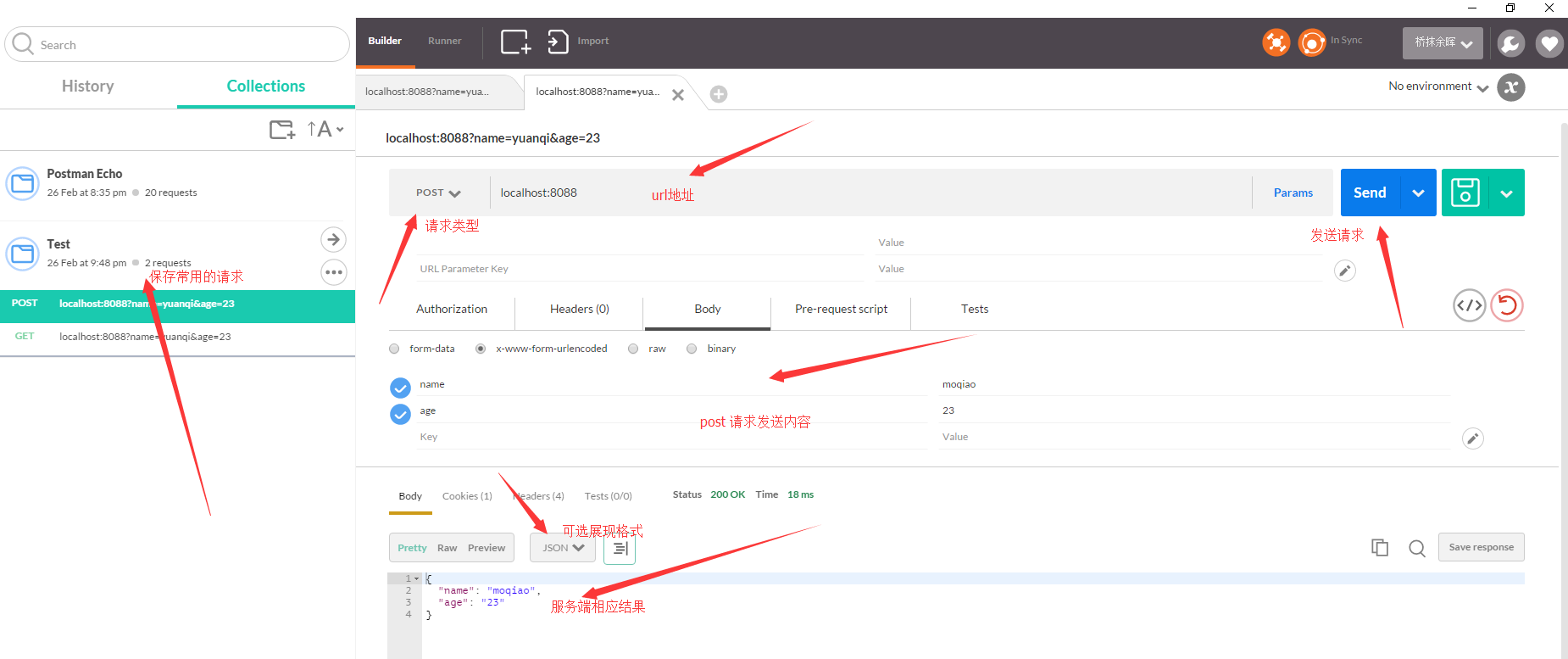 The image above simulates a POST request. After filling in the parameters to send and clicking ‘Send’, you can see that the correct result is returned.
The image above simulates a POST request. After filling in the parameters to send and clicking ‘Send’, you can see that the correct result is returned.
{
"name": "moqiao",
"age": "23"
}GET requests work similarly.
Getting Started with Postman
https://blog.kisnows.com/en-US/2016/02/27/simple-use-of-postman/