Someone shared a set of practice questions in the group, and I decided to use them for some practice.
1. Implement the following layout using HTML5 standards
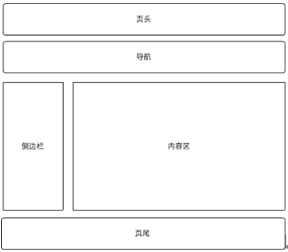
HTML:
<header>HEADER</header>
<nav>NAV</nav>
<aside>ASIDE</aside>
<section>SECTION</section>
<footer>FOOTER</footer>
CSS:
body{
color: white;
font-size: 14px;
text-align: center;
}
header{
background-color: black;
}
nav{
background-color: gray;
}
aside{
width: 30%;
height: 200px;
float: left;
background-color: red;
}
section{
width: 70%;
height: 200px;
margin-left: 30%;
background-color: blue;
}
footer{
background-color: orange;
}2. Write CSS for the responsive layout to achieve the following two scenarios.
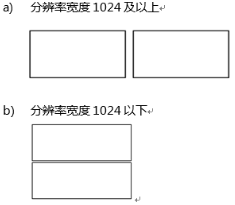
HTML:
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box2">2</div>
CSS:
div{width: 600px;height: 50px}
.box1{background-color: red;}
.box2{background-color: blue;}
@media screen and (min-width:1024px ) {
div{
float: left;
}
}
@media screen and (max-width: 1024px) {
div{
float: none;
}
}3. Implement vertical centering for a line of content containing both images and text (without using table, and consider compatibility).
HTML:
<div class="box1">
<div class="wrap1">
<p>我要居中</p>
<img src="http://images.cnitblog.com/blog/607355/201408/100022249123500.png" alt="liveReload">
</div>
</div>
<div class="box2">
<div class="wrap2">
<p>我也要居中</p>
<img src="http://images.cnitblog.com/blog/607355/201408/100022249123500.png" alt="liveReload">
</div>
</div>
<div class="box3">
<div class="wrap3">
<p>我也要居中</p>
<img src="http://images.cnitblog.com/blog/607355/201408/100022249123500.png" alt="liveReload">
</div>
</div>
CSS:
.box1,.box2,.box3,.box4{
width: 33%;
height: 300px;
float: left;
border: 1px solid #00FFFF
}
/*方法1,用display:table*/
.box1{
display: table;
}
.wrap1{
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
text-align: center;
}
/*方法2,用绝对定位法*/
.box2{
position: relative;
}
.wrap2{
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
border: 1px solid black;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
margin: auto;
}
/*方法3,用translate方法*/
.box3{
position: relative;
}
.wrap3{
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
-webkit-transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
-moz-transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
-ms-transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
-o-transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
}4. Please describe the similarities and differences between cookie, sessionStorage, and localStorage.
Similarities: All are client-side data storage mechanisms. Differences: cookie data is always sent with same-origin HTTP requests (even if not needed), meaning cookies are transmitted back and forth between the browser and the server. In contrast, sessionStorage and localStorage do not automatically send data to the server; they are only stored locally. cookie data also has a path concept, which can restrict a cookie to a specific path. Storage size limits also differ. cookie data cannot exceed 4KB, and because every HTTP request carries cookies, they are only suitable for storing small amounts of data, such as session IDs. While sessionStorage and localStorage also have storage limits, they are much larger than cookies, typically reaching 5MB or more. Data expiration differs. sessionStorage: Only valid until the current browser window is closed, so it cannot persist. localStorage: Always valid; it persists even when the window or browser is closed, making it suitable for persistent data. cookie: Remains valid until its set expiration time, even if the window or browser is closed. Scope differs. sessionStorage is not shared across different browser windows, even for the same page. localStorage is shared across all same-origin windows. cookie is also shared across all same-origin windows.
5. Please identify the performance issues in the following code and optimize it.
var str=" 123";
str +=" 456 ,";
str +=" 789 ,";
str +=" 012" ;I’m not sure how to solve this. -_-
6. Write a user class with the following requirements:
- Properties:
id,name,password,age - Method: Get user information, returning a JSON string
GetUserInfo - Method: Validate user login information, implemented with Ajax, returning a success or failure message for login
CheckLogin - Create an object of the user class and override the
GetUserInfomethod.
Code:
var Person = {
id: "ID",
name: "Name",
password: "PassWord",
$age: null,
get age() {
if (this.$age == undefined) {
return new Date().getFullYear() - 1993;
} else {
return this.$age;
}
},
set age(val) {
if (!isNaN(+val) && +val > 0 && +val < 120) {
this.$age = +val;
} else {
throw new Error(val + "不是正确的年龄");
}
},
GetUserInfo: function () {
return {
id: this.id,
name: this.name,
password: this.password,
age: this.age,
};
},
CheckLogin: function (data, success, error) {
//data为用户数据,success和error分别是成功和失败的回调函数
var xmlhttp;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
//for IE6
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {
if (xmlHttp.responseText === "OK") {
if (typeof success === "function") {
success();
console.log("登陆成功");
}
} else {
error();
console.log("登录错误");
}
}
};
xmlhttp.open("POST", "Login", true);
xmlhttp.setRequestHeader(
"Content-type",
"application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
);
xmlhttp.send(data);
},
};
var me = Object.create(Person);
me.id = "123";
me.name = "kisnows";
me.password = "kPassword";
var myData = me.GetUserInfo();
console.log(myData);
me.GetUserInfo = function () {
console.log("Rewrite GetUserInfo");
};7. jQuery plugin development for a data list page, with the following requirements:
- Odd rows have no background color.
- Even rows have a background color of
#EEE. - When the mouse hovers over a row, the background color becomes
#0066CCand the text color changes to white; revert on mouse out.
Assuming the background is set for li elements under ul, the code is as follows:
(function ($) {
$.fn.extend({
ChageBg: function () {
var lis = $(this).find("li");
var bfBg, bfCl;
for (var i = lis.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
lis[i].index = i;
if (i % 2 === 0) {
$(lis[i]).css("backgroundColor", "#EEE");
// lis[i].style.backgroundColor = '#EEE';
}
$(lis[i]).mouseover(function () {
bfBg = $(this).css("backgroundColor");
// console.log($(this),bfBg)
bfCl = $(this).css("color");
$(this).css({
backgroundColor: "#0066CC",
color: "#FFF",
});
});
$(lis[i]).mouseout(function (pro) {
$(this).css({
backgroundColor: bfBg,
color: bfCl,
});
});
}
},
});
})(jQuery);8. Play a video or audio segment using HTML5 and support segment playback (playing from a specified start time to a specified end time, e.g., for a 10-second video, play from the 2nd second to the 8th second).
HTML:
<video id="video1" controls="controls">
<source src="/example/html5/mov_bbb.mp4" type="video/mp4" />
<source src="/example/html5/mov_bbb.ogg" type="video/ogg" />
Your browser does not support HTML5 video.
</video>I only know how to embed audio/video with controls; I’m unfamiliar with the segment playback feature. I couldn’t find anything online either. I hope someone who knows can tell me how to do it. Thanks.
9. What are the end callback functions for CSS3 transition and animation?
The answer to this question is from the internet http://blog.csdn.net/renfufei/article/details/19617745
transitionendandanimationendevents are the standard browser animation end callback functions. Webkit-based browsers still rely on prefixes, so we must first determine the event prefix before calling it:
/* From Modernizr */
function whichTransitionEvent(){
var t;
var el = document.createElement('fakeelement');
var transitions = {
'transition':'transitionend',
'OTransition':'oTransitionEnd',
'MozTransition':'transitionend',
'WebkitTransition':'webkitTransitionEnd',
'MsTransition':'msTransitionEnd'
}
for(t in transitions){
if( el.style[t] !== undefined ){
return transitions[t];
}
}
}
/* 监听 transition! */
var transitionEvent = whichTransitionEvent();
transitionEvent && e.addEventListener(transitionEvent, function() {
console.log('Transition Complete! Native JavaScript callback executed!');
});
/*
In "whichTransitionEvent", you can replace the text "transition" with "animation" to handle animations (code omitted here...)
*/Summary
- Before attempting question 4, my understanding wasn’t that deep. I only knew that they are all local data stored on the browser side, and that
sessionStorageandlocalStorageare new HTML5 features, withsessionStoragefor short-term storage andlocalStoragefor long-term storage. - I’m not sure how to specifically implement the
CheckLoginmethod in question 6. - I’m unfamiliar with the segment playback feature in question 8.
- I hadn’t heard of question 9 before.
